-
Research Article
-
Score Acquisition Status and Analysis of Land Use and Transportation in Green Building Certified Residential Buildings - Focusing on Certification Trends from 2017 to 2024 -
녹색건축인증 주거용 건축물의 토지이용 및 교통 분야 점수취득현황 및 분석 - 2017~2024년 인증현황을 중심으로 -
-
Seo-Yeon Yang, Kyung-Joo Cho, Yo-Sun Yun, Dae-Hee Jang, Sung-Mo Seo
양서연, 조경주, 윤요선, 장대희, 서성모
- This study examines the score acquisition patterns of the Land Use and Transportation (LT) category in residential buildings certified under the Green …
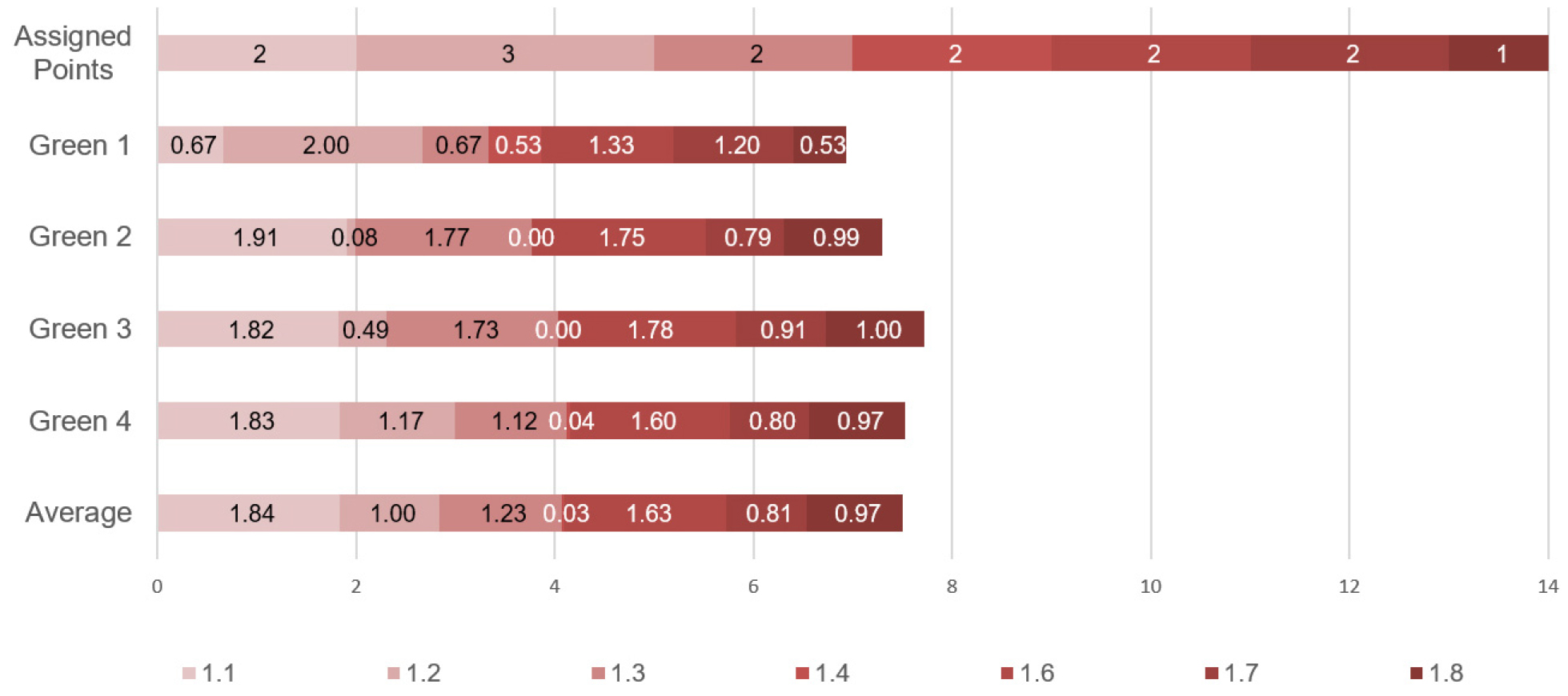
- This study examines the score acquisition patterns of the Land Use and Transportation (LT) category in residential buildings certified under the Green Standard for Energy and Environmental Design (G-SEED) from 2017 to 2024. Using data from 3,018 preliminary certifications for new general and multifamily housing, the analysis investigates average scores, achievement rates, and zero-score distributions across LT assessment items. Results show that both building types consistently achieved high scores in accessibility to certification item 1.8 local amenities and proximity to certification item 1.6 public transportation, indicating that these items are well integrated into current residential planning practices. Conversely, certification item 1.4 validity of solar access protection measures recorded zero-score rates exceeding 95% in both categories due to the difficulty of meeting strengthened north-side maximum angle criteria. Differences between building types were also evident: while general housing frequently achieved high scores in ecological value of certification item 1.1 the existing site, multifamily housing showed notably higher zero-score rates for the same item, reflecting limitations inherent to large-scale site development. The findings provide empirical insight into the operational characteristics of the LT category within the post-2016 G-SEED framework and offer foundational data to support revisions aimed at improving the feasibility and applicability of LT-related assessment items in future residential projects. - COLLAPSE
-
Score Acquisition Status and Analysis of Land Use and Transportation in Green Building Certified Residential Buildings - Focusing on Certification Trends from 2017 to 2024 -
-
Research Article
-
Analysis of Score Acquisition Status of Land Use and Transportation Credits in G-SEED for Non-Residential Buildings - Certification Trends from 2017 to 2024 -
녹색건축인증 비주거용 건축물의 토지이용 및 교통 분야 점수 취득 현황 분석 - 2017~2024년 인증현황을 중심으로 -
-
Kyung-Joo Cho, Yo-Sun Yun, Sung-Mo Seo, Dae-Hee Jang
조경주, 윤요선, 서성모, 장대희
- This study examined the score attainment status of the Land Use and Transportation (LT) category for non-residential buildings—general buildings, office buildings, and …
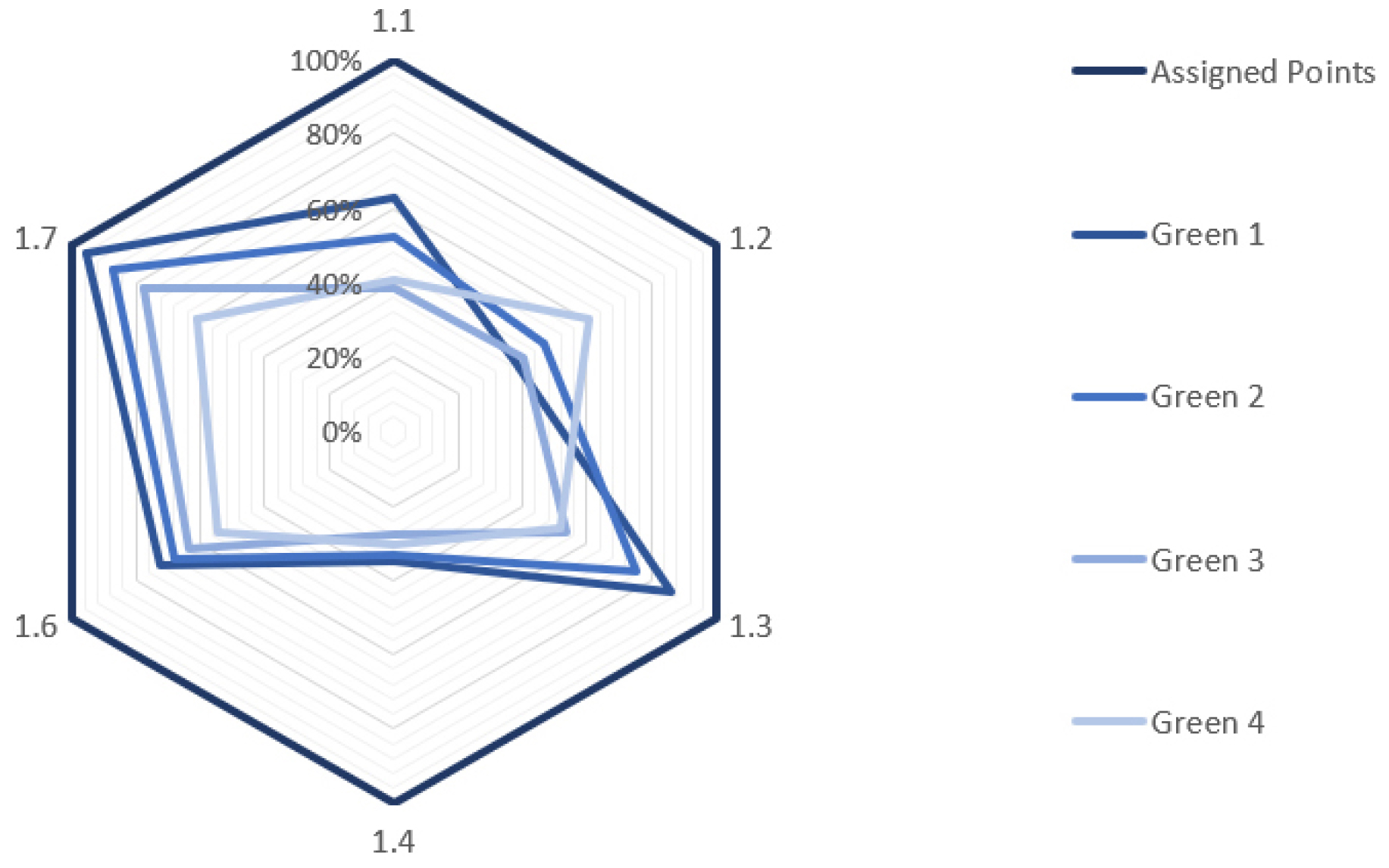
- This study examined the score attainment status of the Land Use and Transportation (LT) category for non-residential buildings—general buildings, office buildings, and school facilities—that obtained G-SEED preliminary certification between 2017 and 2024. The findings are as follows. First, none of the LT items showed an average attainment ratio of 70% or higher across all building types. However, Item 1.7 “Bicycle parking installation” achieved a high average ratio of 78.8% in office buildings and 68.2% in general buildings, whereas school facilities showed a significantly low ratio of 16.3%. Item 1.6 “Proximity to public transportation” showed relatively even ratios across all types (office: 76.4%, general buildings: 58.3%, schools: 58.8%). Second, Item 1.4 “Validity of countermeasures for solar access interference” recorded a zero-score ratio exceeding 50% in all building types, reaching 81% in office buildings, suggesting that solar-access strategies tend to receive lower priority during the design process. Items such as 1.1 “Ecological value of the existing site” and 1.2 “Avoidance of excessive underground development,” which are affected by site conditions and urban density, also showed zero-score ratios above 50% in various building types. These results provide empirical evidence on the current operation of the LT category under the G-SEED system, revised in 2016, and are expected to inform future improvements and updates to the certification framework. - COLLAPSE
-
Analysis of Score Acquisition Status of Land Use and Transportation Credits in G-SEED for Non-Residential Buildings - Certification Trends from 2017 to 2024 -
-
Research Article
-
Exploring Site Planning Characteristics of Apartment Complexes in Small Cities through a ‘Space-form’ Analysis - A Comparative Analysis of Village Residential Areas and Apartment Complexes Using Density, Height, Lot, and Housing Form Indicators -
공간-형태 그래프 분석 기반의 소도시 공동주택 단지계획 특성 연구 - 밀도와 높이, 필지와 주거 형태 분석지표를 통하여 본 마을 주거지와 공동주택 단지 특성 -
-
Ji-Hyun Jo, So-Hyun Park
조지현, 박소현
- The purpose of this study is to analyze regional relationship characteristics in which the planning of apartment complexes in small cities and …
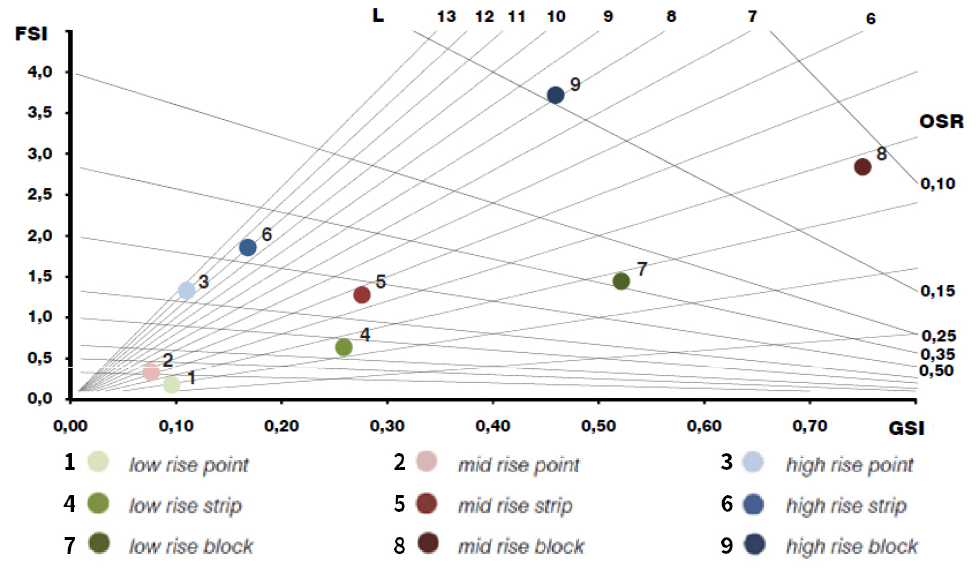
- The purpose of this study is to analyze regional relationship characteristics in which the planning of apartment complexes in small cities and the settlement context of villages are linked. This study analyzed in-depth through density and urban morphological analysis indicators by linking the characteristics of small city’s LH public housing complexes with the context of village settlement, focusing on six completed cases among local cases that have been carried out in small cities nationwide since 2014. As a result of the analysis, first, the village dwellings in the small city have the characteristics of small parcels and low-rise and low-density dwellings with a large number of small-sized building types. The aspect of the village’s residential landscape has an urban-fabric characteristic with a clear cluster of small land occupied by a large number of small one-story detached houses. Second, through density and urban morphological analysis indicators, regional differences were found according to the distribution pattern and cluster degree of housing type, and the landscape difference from village improvement type apartment complexes was different depending on the characteristics of each region. It was found that the larger the relative deviation from the housing cluster according to the regional characteristics of the village dwellings around the analysis target site, the greater the landscape difference of the apartment complex. Third, small city’s multi-family houses are largely divided into various types of housing characteristics in density and urban fabric. - COLLAPSE
-
Exploring Site Planning Characteristics of Apartment Complexes in Small Cities through a ‘Space-form’ Analysis - A Comparative Analysis of Village Residential Areas and Apartment Complexes Using Density, Height, Lot, and Housing Form Indicators -
-
Research Article
-
From Institutions to Care Homes - A Case Study of Residentialization in Danish Profile Nursing Homes -
시설에서 요양형 주택으로 - 요양시설의 주거화에 관한 덴마크 프로필 요양원 사례연구 -
-
Yi-Kyung Hong, Seo Ryeung Ju, Seong Wook Lee
홍이경, 주서령, 이성욱
- This study aims to analyze the spatial planning and operational strategies of three profile nursing homes in Copenhagen, Denmark—Hørgården, Peder Lykke Center, …
- This study aims to analyze the spatial planning and operational strategies of three profile nursing homes in Copenhagen, Denmark—Hørgården, Peder Lykke Center, and Ørestad Plejecenter—and to derive design and operational implications for the development of Korean unit-based long-term care facilities for older adults. The research employed a combination of literature review, field visits, and interviews with facility managers to collect data on spatial planning, design, operation, and management, which were systematically categorized through content analysis to identify characteristics and differences among the cases. The main findings are as follows. First, the separation of housing provision and operation, along with professional management organizations, allowed each facility to implement its own care strategy, ensuring residents’ autonomy and choice. Second, the creation of a home-like environment was achieved through small-scale unit-based living structures, predominantly single-occupancy rooms, and domestic-style kitchens and living spaces, enabling residents to maintain autonomy and individuality while engaging in community life. Third, the active incorporation of natural elements, dementia-friendly design, and multi-sensory stimulation created a therapeutic environment supporting both physical recovery and psychological well-being. Fourth, promoting interaction with the local community emerged as a key feature of Danish nursing homes. These findings demonstrate that Danish long-term care facilities function not merely as institutions but as homes, reflecting a care paradigm that supports older adults’ independence and social integration and provides guidance for Korean long-term care facilities. - COLLAPSE
-
From Institutions to Care Homes - A Case Study of Residentialization in Danish Profile Nursing Homes -
-
Research Article
-
Exploring the Learning Effects of a VR-AI Integrated Information Platform for Age-Friendly Residential Design - A Workshop Study with International Students -
VR-AI 융합형 고령친화 주거공간 조성 정보 플랫폼 활용 학습 효과 탐색 - 국제대학생 대상 교육 워크숍을 토대로 -
-
Yeun-Sook Lee, Tae-Min Kim, Su-Yeon Koh, Mi-Seon Jang
이연숙, 김태민, 고수연, 장미선
- This exploratory study investigates the learning effects of a VR-AI integrated information platform designed to support education on aging-friendly residential environments. As …
- This exploratory study investigates the learning effects of a VR-AI integrated information platform designed to support education on aging-friendly residential environments. As South Korea enters a super-aged society, the need to cultivate positive awareness and evidence-based understanding of elder housing among younger generations has become increasingly urgent. The platform combines immersive VR navigation with generative AI video guides offering multidisciplinary concepts. Six international undergraduate students participated in a short-term intensive workshop where they explored a VR model of an aging-friendly compact dwelling and accessed AI-generated instructional videos embedded at spatial points. Learning outcomes were examined across four dimensions: perceived enjoyment and usefulness, clarity of differentiated levels, changes in attitudes toward elderly housing, and reflections on the combined use of VR and AI. Survey results showed high interest and comprehension, while qualitative responses indicated greater empathy and more positive perceptions of elderly housing. Students also reported that the contextualized AI video guides enhanced engagement by presenting key concepts within spatial locations where such knowledge is most relevant. The findings indicate that VR-AI integrated learning promotes aging-friendly awareness and supports immersive and efficient learning. This study provides preliminary evidence for the applicability of immersive technology in gerontology-related design and for curriculum development in super-aged societies. - COLLAPSE
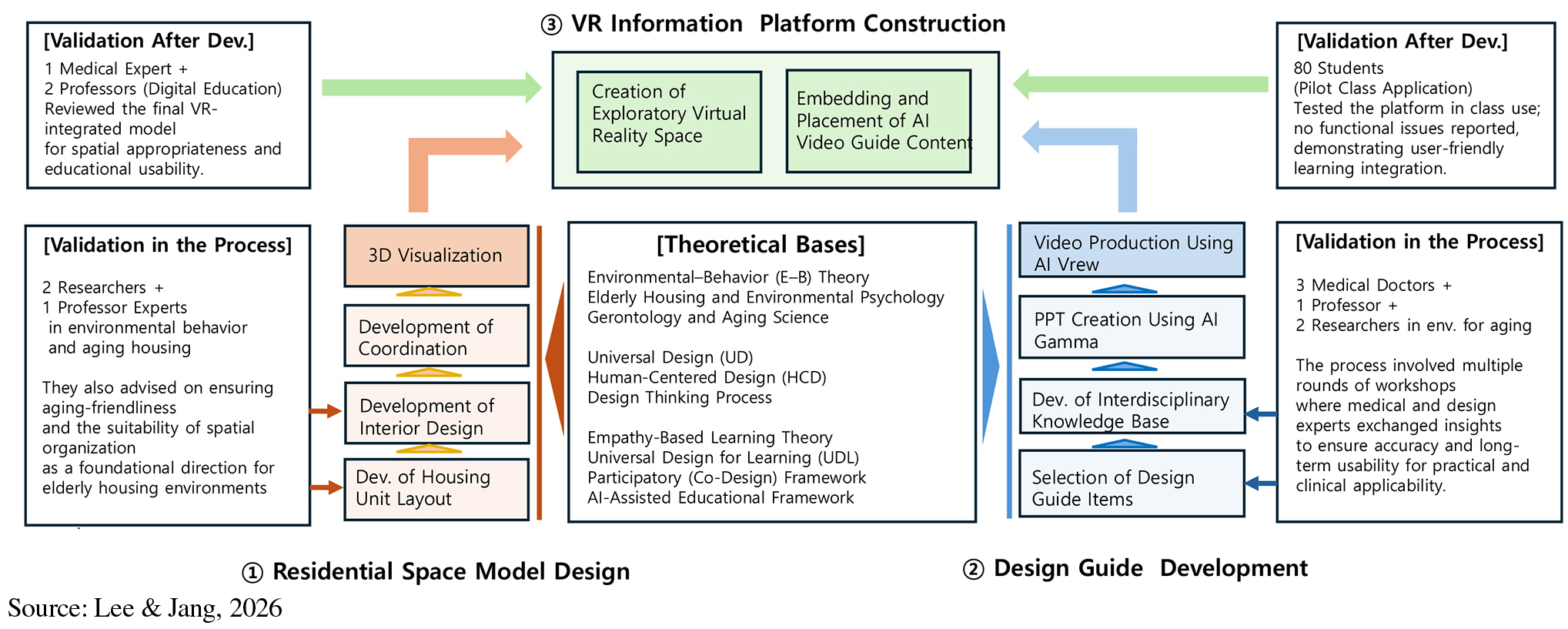
-
Exploring the Learning Effects of a VR-AI Integrated Information Platform for Age-Friendly Residential Design - A Workshop Study with International Students -
-
Research Article
-
Environmental and Social Relationship Changes Through Self-Governance Transition in a Rooftop Community Garden of Senior Residential Living Lab
고령자 공동체주택 리빙랩의 옥상 커뮤니티 정원 자율운영 전환에 따른 물리적 환경 및 사회적 관계 변화
-
Yeunsook Lee, Jaehyun Park, Yumi Hwang
이연숙, 박재현, 황유미
- This study examines the first transition to self-governance in a rooftop community garden within a senior public rental housing community and its …
- This study examines the first transition to self-governance in a rooftop community garden within a senior public rental housing community and its resulting physical and social changes. Using a longitudinal qualitative case design, the analysis triangulated archival records, resident interviews, field observations, and expert assessments of landscape and ecological quality. The transition followed a trajectory of allocation, norm vacuum, ecological and sensory degradation, and subsequent attempts at recovery. Night-time relocations of favored plants, zone-based ownership signals, and vegetable monoculture disrupted the intended ecological rhythm and seasonality of the garden, while fertilizer misuse degraded olfactory comfort and reduced stay duration. Socially, participation fragmented into active, intermittent/neglect, and observer groups, accompanied by disputes over harvest rights, leadership frictions, and avoidance behaviors. These tensions revealed limits of participation-heavy models without codified rules or procedural safeguards. Over time, residents reframed the garden as a shared asset and converged on institutional scaffolding such as a wayfinding planting map, one-page rules, short learning-feedback loops, and low-cost dispute-resolution mechanisms. The findings show that rooftop community gardens function as essential physical, social, and operational infrastructure within senior community housing, shaping ecological quality, social cohesion, and everyday wellbeing. Ultimately, effective self-governance depends less on participation volume than on visible rules, procedural fairness, embedded learning, and mediation structures that stabilize shared spaces in super-aged societies. - COLLAPSE
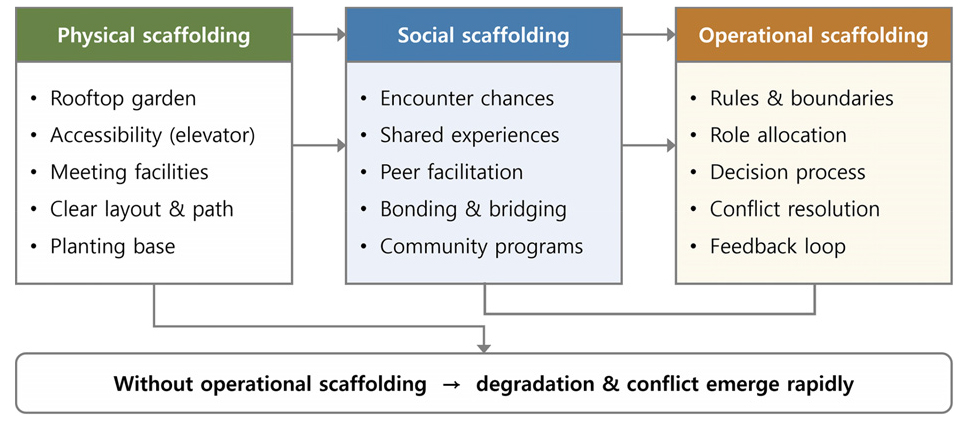
-
Environmental and Social Relationship Changes Through Self-Governance Transition in a Rooftop Community Garden of Senior Residential Living Lab
-
Research Article
-
An Exploratory Case Study on the Effects of Age-Friendly Home Modifications Using Sensor-Based Activity Data
센서 기반 활동량 자료를 활용한 고령친화 주택개조의 탐색적 사례 연구
-
Yongmin Lee, Ji-Soo Yim
이용민, 임지수
- Aging in Place (AIP) has emerged as a key policy objective, emphasizing the importance of age-friendly home modifications that enable older adults …
- Aging in Place (AIP) has emerged as a key policy objective, emphasizing the importance of age-friendly home modifications that enable older adults to live safely and independently. Despite growing policy interest, empirical evidence on the actual effects of such modifications remains limited. This study empirically examines the impact of age-friendly home modifications on daily activity levels, subjective safety perceptions, and AIP awareness among older adults. The analysis focuses on eight single-person households participating in the “iH-type Customized Age-Friendly Home Modification Program.” Daily activity data were collected using motion sensors installed in bedrooms, bathrooms, and entrances for two weeks before and after the modifications. In addition, structured interviews were conducted to assess changes in perceived safety and AIP-related awareness.Results show that overall daily activity levels increased following the modifications, with notable increases observed in bedrooms and entrances. In some cases, reduced activity reflected the elimination of unnecessary or unstable movements, indicating improved safety and movement efficiency rather than functional decline. Subjective perceptions of mobility, physical and emotional safety, and the usability of assistive devices improved, while perceived fall risk decreased. Awareness of AIP—particularly regarding continued residence and housing suitability—also increased substantially. These findings provide empirical evidence that age-friendly home modifications enhance both functional activity and psychological safety, supporting AIP. - COLLAPSE

-
An Exploratory Case Study on the Effects of Age-Friendly Home Modifications Using Sensor-Based Activity Data
-
Research Article
-
An Analysis of Program Needs for Aging in Place among Older Residents in Permanent Rental Housing
영구임대주택 고령 거주자의 지역사회 정주 지원을 위한 프로그램 요구 분석
-
Mi-Seon Jang, Min-Seo Kim, Soo-Bin Kang
장미선, 김민서, 강수빈
- This study aimed to examine service program needs to support Aging in Place(AIP) among older adults living in aging permanent rental housing …
- This study aimed to examine service program needs to support Aging in Place(AIP) among older adults living in aging permanent rental housing complexes, where resident aging and housing deterioration have progressed simultaneously. A face-to-face survey was conducted over four days in May 2025 with residents aged 65 years and older in two permanent rental apartment complexes in Jeonju, South Korea, and 152 valid responses were analyzed. The results showed that respondents’ intention to age in place was very high (mean = 4.66/5). Program needs were relatively higher in the domains of housing management and housing life (3.68) and medical and health support (3.58), whereas needs were lower for employment and economic activity support (2.66) and leisure, education, and social participation support (2.97). At the item level, strong demands were identified for programs focused on maintaining daily functioning and health, including physical therapy services, health management services, household hygiene management, and emergency call and welfare check services. Although the overall perceived necessity of AIP support programs was moderately high (mean = 3.64), willingness to pay was limited, with a strong preference for free services. These findings provide foundational evidence for establishing program priorities and developing low-cost, coordinated operational models to support AIP among older residents in permanent rental housing. - COLLAPSE

-
An Analysis of Program Needs for Aging in Place among Older Residents in Permanent Rental Housing
-
Research Article
-
Korea and Other Countries’ Supportive Programs for Semi-Basement Housing and Residents - Focusing on Case Studies and Interviews with US Officials -
반지하 주택 관련 국내외 주택 및 거주자 지원 프로그램 분석 연구 - 사례분석 및 미국 공무원 면담조사를 기반으로 -
-
Suk-Kyung Kim, Jongdae Jung, Eunjoo Lee
김석경, 정종대, 이은주
- The purpose of this study is to examine domestic and foreign codes and regulations regarding semi-basement housing units, and to suggest improvements …
- The purpose of this study is to examine domestic and foreign codes and regulations regarding semi-basement housing units, and to suggest improvements needed for safe use as housing. Keyword searches from foreign codes and regulations and in-person interviews with HUD officials were conducted. As a result of reviewing the current building and residential codes and regulations of vulnerable housing, focusing on semi-basement housing, the identified problems were related to 1) minimum standards for indoor and outdoor environments that were not suitable for residency and 2) the evacuation and fire safty standards that were difficult to apply to the half-basement units. Above all, considering that semi-basement housing units are vulnerable to flooding and fire, it is urgent to prepare safety-related standards for this type of dwellings. Inclusive and detailed codes and regulations should be established so that these units can serve as safe housing in the future. - COLLAPSE
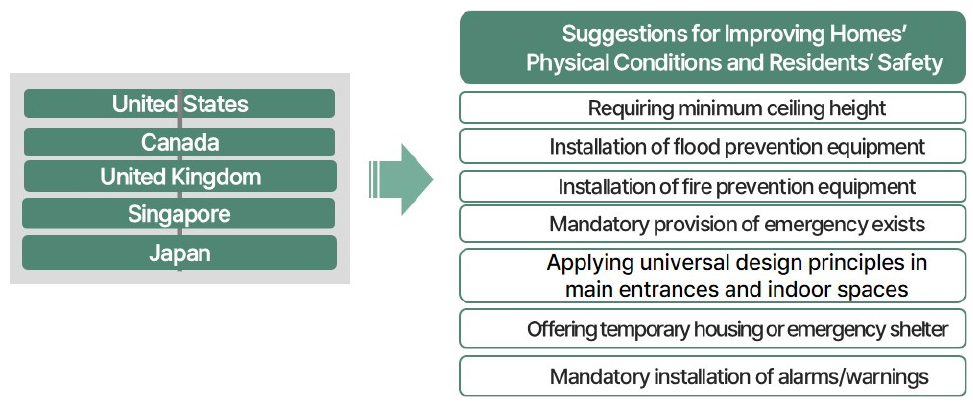
-
Korea and Other Countries’ Supportive Programs for Semi-Basement Housing and Residents - Focusing on Case Studies and Interviews with US Officials -
-
Research Article
-
A Study of Village Representatives’ Perceptions of Housing Problems and Housing Policy Support in Rural Areas
농촌 지역 주거문제와 주거정책 지원에 대한 마을 주민 대표 인식 연구
-
Mi-Seon Jang
장미선
- This study aims to explore housing problems in rural areas from the perspective of local representatives and to derive directions for appropriate …
- This study aims to explore housing problems in rural areas from the perspective of local representatives and to derive directions for appropriate housing support. A survey was conducted with village representatives in a county-level rural area in Jeollabuk-do, Republic of Korea, and a total of 61 responses were analyzed. The findings indicate that housing problems in rural areas are perceived as structural issues resulting from the combined effects of housing cost burdens, an increasing number of deteriorated houses, and shortages of public rental housing and living infrastructure. Housing problems were primarily identified through individual complaints, while village representatives mainly played a role in conveying these issues to administrative authorities during the resolution process. Perceptions regarding the potential for population inflow following the resolution of housing problems were divided between positive and negative views. The most frequently identified effective housing support measures were the supply of senior welfare housing and public rental housing. This study provides exploratory and context-specific evidence to inform the development of rural housing policies that incorporate the perspectives of local representatives. - COLLAPSE

-
A Study of Village Representatives’ Perceptions of Housing Problems and Housing Policy Support in Rural Areas
-
Research Article
-
Analysis of the Relationship Between Population Structure Changes and Urban Functional Balance
인구구조 변화와 도시 기능 균형과의 관계성 분석
-
Ning Xue, Jeong-Won Lee, Ji-Eun Seo
슈에닝, 이정원, 서지은
- This study analyzes panel data from 17 metropolitan regions in Korea (2014-2023) to examine how demographic structures influence the spatial equity of …
- This study analyzes panel data from 17 metropolitan regions in Korea (2014-2023) to examine how demographic structures influence the spatial equity of urban functional spaces. Using the Structural Variation Coefficient (SVC), correlation analysis, and multiple regression, the study identifies the impacts of aging, population density, population growth, migration, and birth rates on five key urban functions: medical, educational, green, commercial, and public services. The analysis results showed that “aging rate” showed a significant relationship with “medical facilities,” “educational facilities,” and “green space.” “Population density” and “birth rate” also showed significant relationships with “public service facilities.” “Population growth rate” showed a significant relationship with “medical facilities” and “green space.” Meanwhile, “net migration rate” showed no significant relationship with any urban function variable. Based on these findings, the study proposes strategic directions for restructuring urban functions to address Korea’s ongoing demographic transition. - COLLAPSE
-
Analysis of the Relationship Between Population Structure Changes and Urban Functional Balance
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of the Korean Housing Association
Journal of the Korean Housing Association
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of the Korean Housing Association
Journal of the Korean Housing Association









