-
Research Article
-
Analysis of Unit Care Design Guidelines for Long Term Care Facilities from the Perspective of Person-Centered Care (PCC)
인간중심케어(Person-Centered Care) 관점에서 본 노인요양시설의 유니트케어 디자인가이드라인 분석
-
Yi-Kyung Hong, Seo Ryeung Ju, Seong Wook Lee
홍이경, 주서령, 이성욱
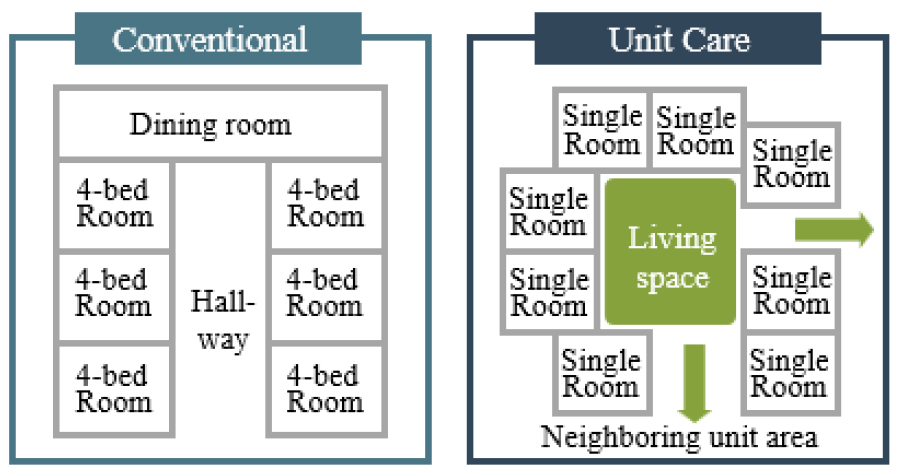
- This study quantitatively analyzes design guidelines for Unit Care nursing homes from the perspective of Person-Centered Care (PCC), focusing on how spatial …
- This study quantitatively analyzes design guidelines for Unit Care nursing homes from the perspective of Person-Centered Care (PCC), focusing on how spatial design reflects the core PCC dimensions of autonomy, everydayness, relationships, integration, and meaning. A total of 75 guideline items were classified by spatial type (overall facility, shared spaces, private rooms) and design elements (spatial planning, design details, equipment and devices), then evaluated for their relevance to PCC concepts. Results showed that autonomy and everydayness were strongly emphasized, highlighting design efforts to support residents’ independence and continuity of daily life. Conversely, relationships and meaning were less reflected, indicating a need to better incorporate social interaction and emotional significance into environmental design. Cross-national comparisons revealed that Canada, the United States, and the UK prioritized autonomy and everydayness, whereas Japan placed relatively greater emphasis on relationships and meaning, reflecting cultural differences. The findings underscore the importance of adopting a multidimensional approach that integrates physical, social, and emotional aspects in the design of Unit Care facilities. This research provides foundational insights for developing comprehensive PCC-oriented design guidelines and operational strategies aimed at enhancing quality of life for older adults. - COLLAPSE
-
Analysis of Unit Care Design Guidelines for Long Term Care Facilities from the Perspective of Person-Centered Care (PCC)
-
Research Article
-
A Case Study on the Conversion of Urban Idle Spaces in China into Elderly Care Facilities for a Super-Aged Society
초고령 사회 대응을 위한 중국 도시 유휴공간의 노인요양시설 개조사례 연구
-
Fei Hao, Miryum Chung
하오페이, 정미렴
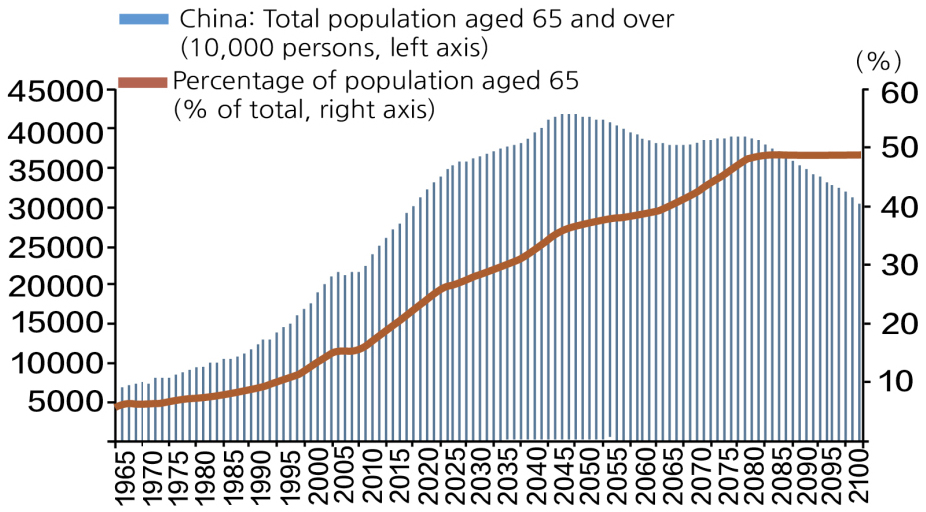
- To address the challenges of China’s impending super-aged society, this study examines three cases in Zhejiang Province where a former primary school, …
- To address the challenges of China’s impending super-aged society, this study examines three cases in Zhejiang Province where a former primary school, a community center, and a department store were converted into elderly care facilities. The analysis is guided by national design standards and a researcher-developed evaluation framework, systematically comparing the features and shortcomings of age-friendly adaptations across different types of urban idle spaces. The research focuses on key aspects such as spatial layout, barrier-free facilities, smart and safety systems, and integration with regional resources. The results indicate that although all three cases meet the basic requirements of national standards, structural limitations and implementation challenges have led to deficiencies in functional zoning, barrier-free details, and resource utilization. Based on these findings, the paper proposes optimization strategies tailored to different space types, providing practical references and theoretical support for the high-quality transformation of urban idle spaces into elderly care facilities. - COLLAPSE
-
A Case Study on the Conversion of Urban Idle Spaces in China into Elderly Care Facilities for a Super-Aged Society
-
Research Article
-
A Study on Management Strategies in Mixed Tenure Housing Complexes for Social Integration - A Case Study of Haengbok Housing Complex -
사회통합적 관점에서 분양・임대 혼합주택단지 관리제도 개선방안 연구 - LH 행복주택 혼합단지를 중심으로 -
-
Seungyeoun Cho, Nansoon Eun, Minchan Choi
조승연, 은난순, 최민찬
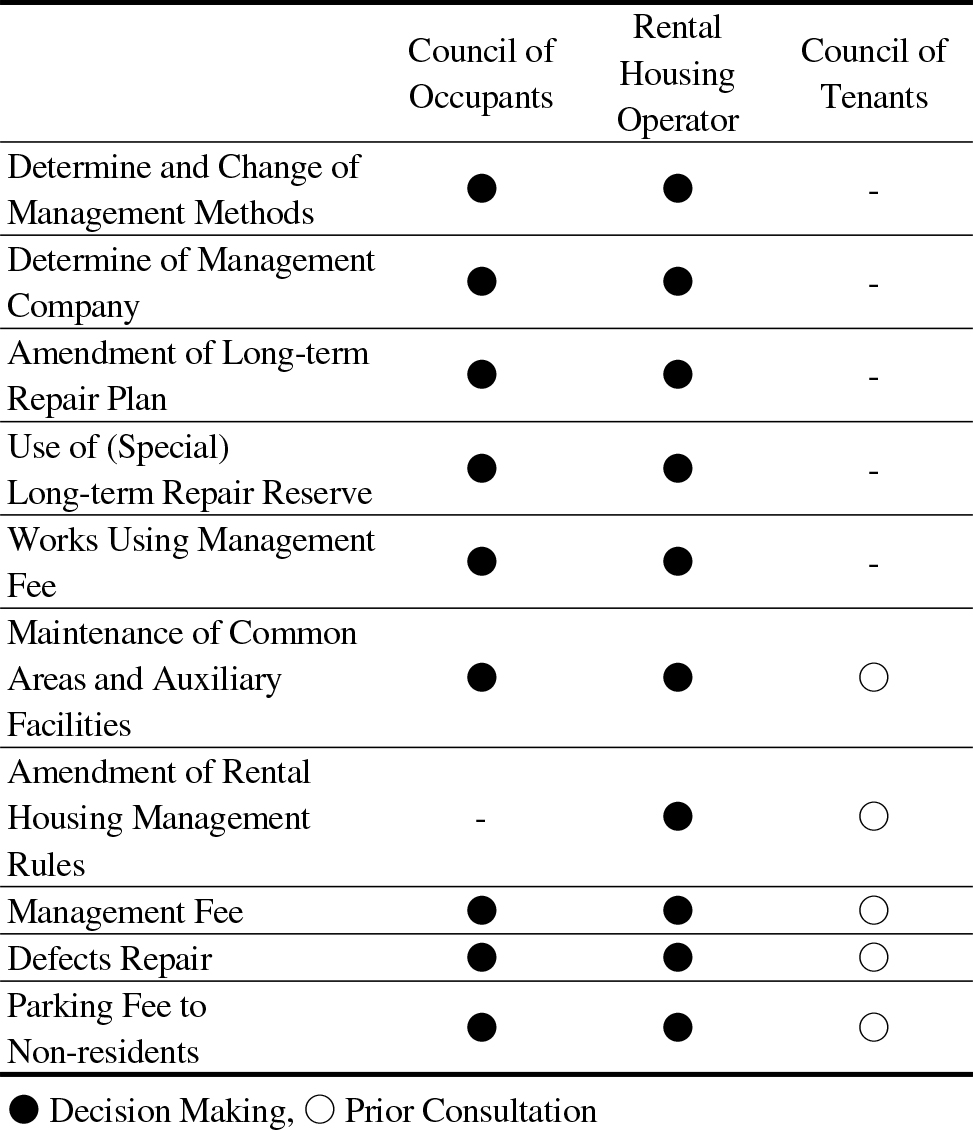
- This study explores strategies to enhance tenant participation and promote social integration in mixed-tenure housing complexes in South Korea. Since the 2000s, …
- This study explores strategies to enhance tenant participation and promote social integration in mixed-tenure housing complexes in South Korea. Since the 2000s, public rental housing supply has increased, but social exclusion of rental tenants remains a concern. To mitigate segregation, the government has encouraged mixed-tenure developments integrating owner-occupied and rental units. However, governance challenges persist, as resident councils are often dominated by owners, and tenant representation is weak or inconsistent. The lack of on-site public housing personnel further reinforces unequal decision-making structures. To address these issues, the study combines legal and institutional reviews with empirical analysis based on 20 field investigations and an online survey of 8,995 residents across 35 LH-developed mixed-tenure complexes, yielding 1,181 valid responses (13% response rate). Results reveal key barriers to tenant participation, including unequal representation, inadequate institutional support, and biased conflict resolution systems. The study proposes reforms to strengthen participatory governance, ensure fair tenant representation, and improve management transparency. These measures aim to foster inclusive community relations and equitable governance structures, contributing to broader policy discussions on using mixed-tenure housing as a foundation for sustainable social integration in Korea. - COLLAPSE
-
A Study on Management Strategies in Mixed Tenure Housing Complexes for Social Integration - A Case Study of Haengbok Housing Complex -
-
Research Article

-
Assessing the Housing Environment of Older Adults from a Healthy Community Design Perspective
건강한 커뮤니티 디자인 관점에서 본 중고령자의 주거환경 평가
-
Young-Ho Yoon, Mi-Seon Jang
윤영호, 장미선
- This study aimed to examine the perceived needs for improvement and environmental preferences among middle-aged and older adults, in response to the …
- This study aimed to examine the perceived needs for improvement and environmental preferences among middle-aged and older adults, in response to the growing demand for age-friendly housing environments in the context of Korea’s transition to a super-aged society. The survey targeted individuals aged 50 and over, including both baby boomers and older generations, across various regions in South Korea. A total of 473 valid responses were collected through an online questionnaire. The analysis revealed a high level of demand for improvements in physical and environmental conditions, particularly concerning aged housing, limited parking space, fine dust, noise issues, and poor energy efficiency. Respondents also expressed strong preferences for environmental features conducive to health and well-being, such as clean and pleasant surroundings and opportunities for interaction with nature. Moreover, notable differences were observed in both needs and preferences based on individual characteristics such as gender, age, region, housing type, and perceived economic status. These findings highlight the importance of tailored housing policies and designs that reflect the diverse conditions and experiences of older adults. This study provides empirical evidence to inform the development of age-friendly residential environments and underscores the need for localized and group-specific policy interventions. - COLLAPSE
-
Assessing the Housing Environment of Older Adults from a Healthy Community Design Perspective
-
Research Article
-
Multidimensional Exploration of Indoor Color Environments and The Emotional and Cognitive Response - A Systematic Literature Review of Empirical Studies Based on EEG -
실내 환경의 색채와 감정 및 인지반응에 대한 다차원적 탐색 - 뇌파 기반의 실증연구 문헌 분석 -
-
Xin Wang, Ji Young Cho
왕흠, 조지영
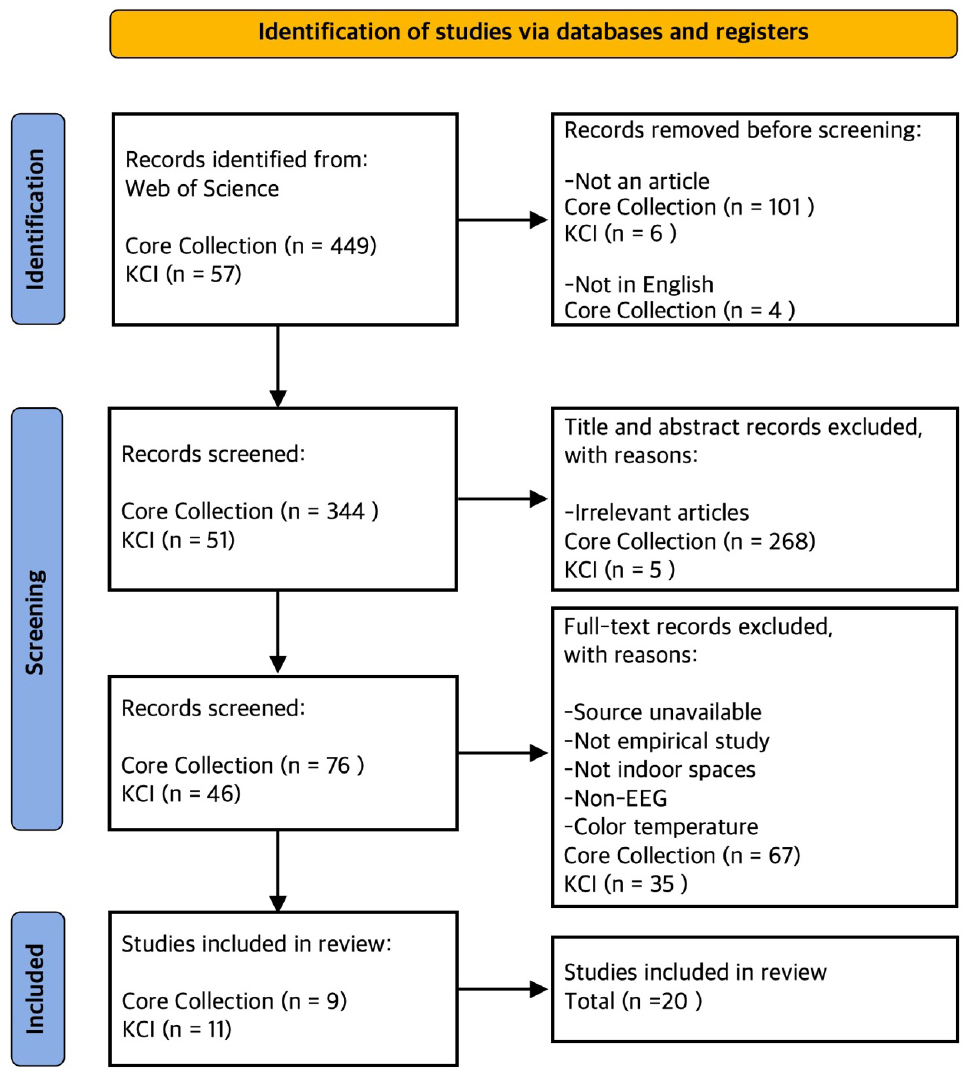
- This study systematically reviews EEG-based empirical research on the effects of indoor color with the Stimulus-Organism-Response framework. Following Preferred Reporting Items for …
- This study systematically reviews EEG-based empirical research on the effects of indoor color with the Stimulus-Organism-Response framework. Following Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines, 20 peer-reviewed experimental studies were analyzed in terms of stimuli characteristics, research design, EEG indicators, and associated psychological and behavioral responses. The results show that (1) the stimuli used in the experiment were mainly walls with different colors applied to various types of spaces; (2) cool hues (blue/green) commonly increase alpha activity, supporting relaxation, while warm hues (red/yellow) more often elevate beta/gamma activity, reflecting arousal and engagement; (3) these effects are moderated by the function of the space, stimulus properties, presentation mode, and participant state; and (4) cool colors tend to promote calm affect and, in some contexts, better task performance, whereas warm colors tend to enhance engagement but also raise tension or error rates. This review concludes that color effects are context-dependent and highlights the need for standardized protocols to enable reproducible and evidence-based design guidance. - COLLAPSE
-
Multidimensional Exploration of Indoor Color Environments and The Emotional and Cognitive Response - A Systematic Literature Review of Empirical Studies Based on EEG -
-
Research Article
-
Characteristics of Common Facilities Planning in Apartment Complexes for Use as Elderly Welfare Facilities - Focusing on the Dongnam District of Cheongju -
노인복지시설로의 활용을 위한 아파트단지 부대복리시설 배치 유형과 특성 - 청주시 동남지구 사례 -
-
Su-Bin Yu, Nahyang Byun
유수빈, 변나향
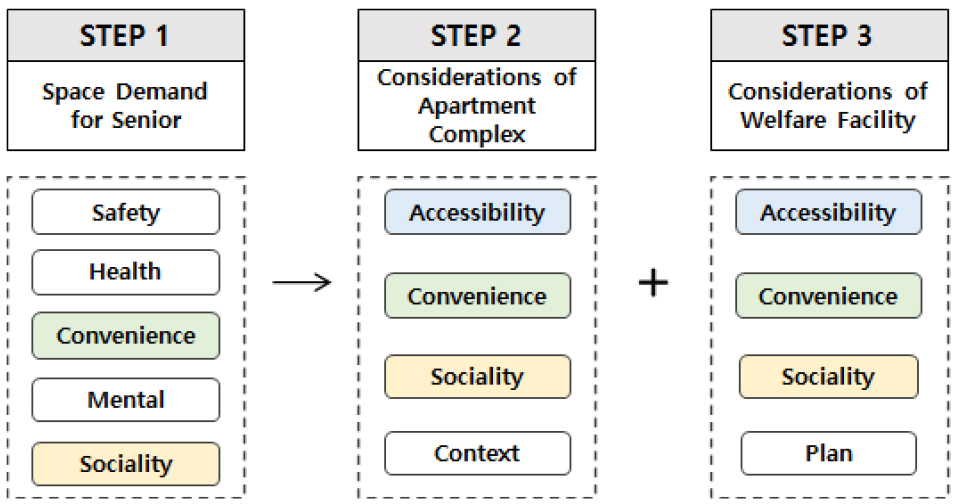
- Currently, the unprecedentedly rapid aging is leading to the aging of apartment members, and the demand for the complex environment, especially the …
- Currently, the unprecedentedly rapid aging is leading to the aging of apartment members, and the demand for the complex environment, especially the auxiliary welfare facilities that are shared spaces, as residential spaces for the elderly is also increasing. However, the auxiliary welfare facilities for elderly residents of existing apartments exist only as senior citizens. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to establish basic data for using the auxiliary welfare facilities of apartments in response to an ultra-aging society. Considerations for facilities supporting the elderly in apartment complexes were derived based on the previous research theory that reviewed the leisure activities and needs of the elderly. As a research method, the characteristics of the two space ranges were analyzed, with the considerations derived above for apartment complexes and auxiliary welfare facilities as an analysis framework. As a result of the study, several types could be derived into the layout type and facility plane type, and different characteristics were shown in many ways such as accessibility, convenience, and sociality, which are considerations. These analysis results can be referred to in the process of planning elderly welfare facilities when existing facilities are used as welfare facilities for the elderly. - COLLAPSE
-
Characteristics of Common Facilities Planning in Apartment Complexes for Use as Elderly Welfare Facilities - Focusing on the Dongnam District of Cheongju -
-
Research Article

-
Operational Practices of Senior Welfare Centers in Enhancing Disaster and Safety Competence among Senior
노인의 재난・안전 역량 강화 교육을 위한 노인복지관 운영 현황
-
Seong-Kyung Choi, Jeong-Min Moon
최성경, 문정민
- This study investigates strategies for linking community spaces and facilities to enhance disaster safety competence among older adults in the context of …
- This study investigates strategies for linking community spaces and facilities to enhance disaster safety competence among older adults in the context of rapid aging, climate change, and evolving socio-technical environments. Through a theoretical review, it examines disaster vulnerability, safety competence, and the characteristics of community care facilities that support safety education for older adults. Key educational elements—target groups, venues, methods by disaster type and phase, and operational practices—were identified. Based on these, disaster safety education programs at five senior welfare facilities in Gwangju Metropolitan City were analyzed. The results show that programs primarily targeted facility users and staff, utilizing both indoor and outdoor spaces, but lacked dedicated disaster safety facilities. The content mainly focused on everyday safety topics such as fire, earthquakes, first aid, fall prevention, and traffic safety, with emphasis on preparedness and response phases, while prevention and recovery phases were underrepresented. Most programs were conducted in collaboration with fire departments and public agencies. The study recommends developing specialized education spaces, diversifying program content, strengthening recovery-phase training, and fostering integrated operations with nearby community facilities to improve older adults’ disaster response capacity. - COLLAPSE
-
Operational Practices of Senior Welfare Centers in Enhancing Disaster and Safety Competence among Senior
-
Research Article
-
A Study on the Design of a Management Quality Evaluation Framework for Non-Mandatory Management Residential Condominiums - Focusing on an Importance Analysis based on AHP and Likert Scale -
비의무관리대상 주거용 집합건물의 관리품질 평가항목 체계 설계에 관한 연구 - AHP 및 리커트 기반 중요도 분석을 중심으로 -
-
Nack-Jin Sung, Woong-Kyoo Bae, In-Sun Park
성낙진, 배웅규, 박인선
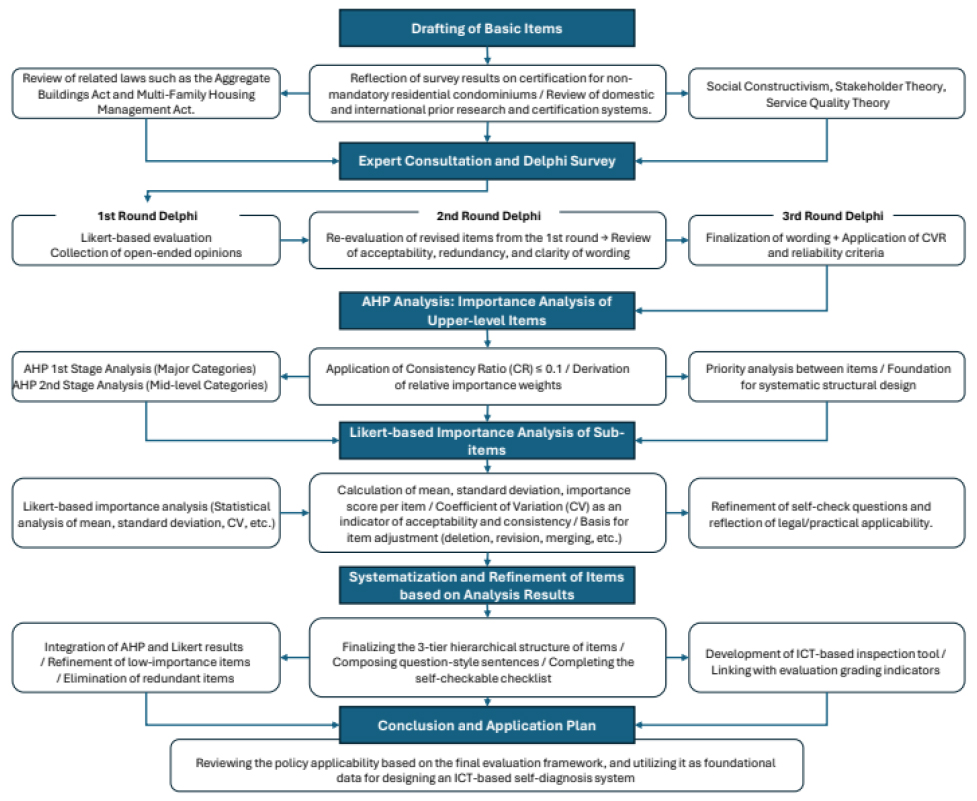
- This study aims to address the poor management of non-mandatory management residential collective buildings, which fall outside the scope of the 「Multi-Family …
- This study aims to address the poor management of non-mandatory management residential collective buildings, which fall outside the scope of the 「Multi-Family Housing Management Act」. Its purpose is to develop a comprehensive evaluation framework with item-specific weights that can objectively diagnose management quality and guide autonomous improvement. To achieve this, a final set of evaluation items—comprising five major categories, 21 mid-level categories, and 118 sub-categories—was established through a literature review, legal analysis, and three rounds of an expert Delphi survey. Subsequently, the relative weights for the upper-tier categories were calculated using the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP), while a Likert scale analysis measured the absolute importance of the sub-categories. The results indicate that ‘Safety and Disaster Prevention Management’ and ‘Building and Facility Management’ were of the highest importance. Notably, a perception gap emerged between the AHP (long-term importance) and Likert (short-term urgency) analyses, revealing a tension between preserving physical asset value and establishing fundamental governance procedures. This study holds academic significance as the first to present an integrated weighting model specifically tailored for these non-mandatory management buildings. Moreover, it offers practical implications, as the developed framework can provide foundational data for developing ICT-based self-diagnosis tools and provide an empirical basis for relevant policymaking. - COLLAPSE
-
A Study on the Design of a Management Quality Evaluation Framework for Non-Mandatory Management Residential Condominiums - Focusing on an Importance Analysis based on AHP and Likert Scale -
-
Research Article

-
Spatial Characteristics and Design Trends of Fine Stays in South Korea - A Study of Top-Ranked Accommodations on the Stayfolio Platform -
국내 파인 스테이 공간 특성 및 디자인 경향 분석 - 스테이폴리오 숙박 플랫폼의 상위권 숙박시설을 대상으로 -
-
Naeun Gu
구나은
- This study analyzes the spatial characteristics and design trends of 29 top-ranked stays on Stayfolio, a curated accommodation platform, reflecting the current …
- This study analyzes the spatial characteristics and design trends of 29 top-ranked stays on Stayfolio, a curated accommodation platform, reflecting the current lodging culture that emphasizes spatial design and emotional experience. The analysis revealed that 22 out of the 29 stays are located in Jeju and Gangwon provinces, with a nearly equal proportion of remodeled old houses and newly constructed buildings. In terms of spatial characteristics, 72.4% of the stays consisted of fully independent buildings, and 62.1% featured a massing form with a pitched roof covering the entire volume. Functionally, most stays included transitional spaces such as yards, central courtyards, or terraces that connect the interior and exterior, while more than half provided water-related facilities such as jacuzzis or swimming pools. Regarding design elements, wood, tile, and glass were the most commonly used interior materials, and white, brown, and gray appeared prominently across all stays. In terms of design styles, the modern style was the most prevalent, often combined with traditional Korean design elements or localized features expressed through contemporary design. Among detailed design features, the emphasis and variation of openings as well as boundary-defining elements appeared most frequently. Future research is expected to expand the scope to a larger number of stays and incorporate users’ actual experiences for deeper insights. - COLLAPSE
-
Spatial Characteristics and Design Trends of Fine Stays in South Korea - A Study of Top-Ranked Accommodations on the Stayfolio Platform -
-
Research Article
-
The Impact of Housing Price Inequality on Middle-aged Adults’ Perceptions of Social Mobility - Focusing on the Moderating Effect of Social Capital -
주택가격 불평등이 중년층 계층이동 가능성 인식에 미치는 영향 - 사회적 자본의 조절효과를 중심으로 -
-
Young-hyun Shin, Ayoung Woo, Ja-hoon Koo
신영현, 우아영, 구자훈
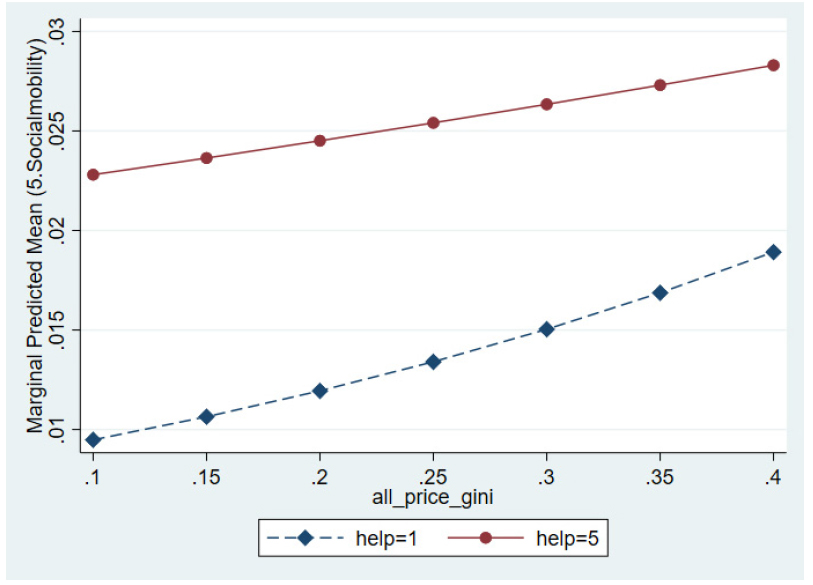
- This study aims to examine the effect of housing price inequality on perceptions of socioeconomic mobility and to analyze the moderating role …
- This study aims to examine the effect of housing price inequality on perceptions of socioeconomic mobility and to analyze the moderating role of social capital. For this purpose, data from the Seoul Survey (2018-2023) were utilized, and a multilevel ordered logistic regression model was employed to simultaneously account for both individual- and district-level variables. The analysis revealed that middle-aged groups tend to perceive socioeconomic mobility more positively as housing price inequality intensifies, and the effects of social capital differed by specific factors. In particular, help, altruism, and trust in government were found to mitigate the impact of inequality, whereas trust in friends and neighbors amplified it. These findings highlight the necessity of considering the conditional effects of social capital when examining the relationship between housing price inequality and mobility perceptions, and they suggest that policy approaches should reflect both the specific characteristics of middle-aged groups and the variations in the type and level of social capital. - COLLAPSE
-
The Impact of Housing Price Inequality on Middle-aged Adults’ Perceptions of Social Mobility - Focusing on the Moderating Effect of Social Capital -
-
Research Article
-
Neighborhood Environment and Residential Intention in Seoul Before and After COVID-19 - Social Capital Pathways Across Age Groups -
COVID-19 팬데믹 전후 서울시 근린환경과 지속거주의향의 구조적 연관성 - 연령대별 사회적 자본 경로 분석 -
-
Hee-Ran Cho, Ja-Hoon Koo, Hyungun Sung
조희란, 구자훈, 성현곤
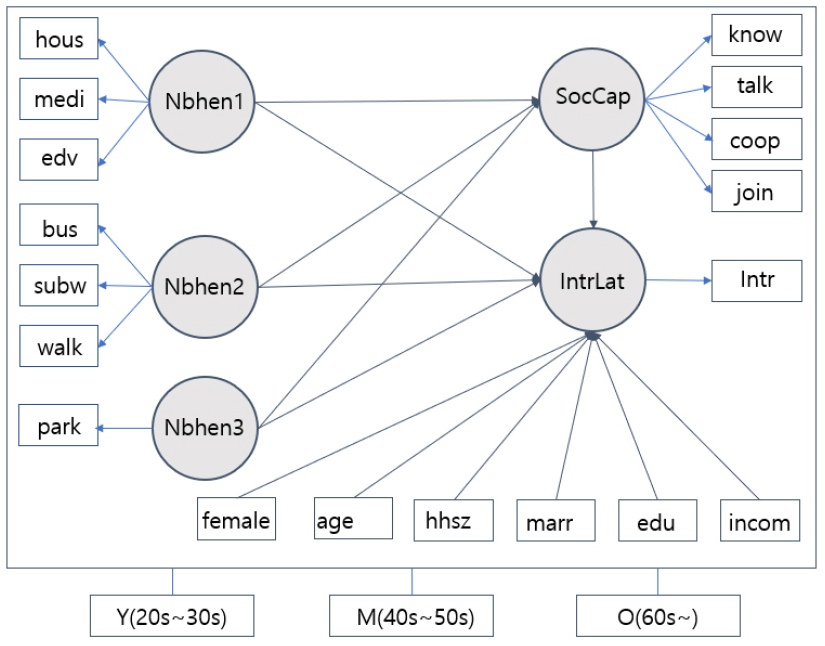
- This study examines how neighborhood-environment perceptions and social capital are structurally related to residential intention and compares age-group path differences among Seoul …
- This study examines how neighborhood-environment perceptions and social capital are structurally related to residential intention and compares age-group path differences among Seoul residents before and after COVID-19 (2018, 2023). Pre-pandemic, only older adults showed significant direct effects of all neighborhood-environment factors on residential intention, whereas youth and middle-aged groups were significant on selected paths. The mediating effect of trust-based social capital was positive but limited to older adults. Post-pandemic, the significance of transport, walkability, and green-space paths increased across all ages; green-space effects were strongest for older adults but significant and negative for youth. Public transport and walkability were salient for youth, while housing, medical care, and education were more salient for the middle-aged. Communication- and participation-based social capital showed negative or non-significant associations with residential intention across all ages, and mediation via social capital was likewise negative or non-significant. These findings delineate post-pandemic shifts in age-specific policy priorities and in the composition of social capital, providing an empirical basis for tailored housing policies and community recovery. - COLLAPSE
-
Neighborhood Environment and Residential Intention in Seoul Before and After COVID-19 - Social Capital Pathways Across Age Groups -
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of the Korean Housing Association
Journal of the Korean Housing Association
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of the Korean Housing Association
Journal of the Korean Housing Association









