-
Research Article
-
A Study on Converting Underutilized Spaces into Elderly Care Facilities in Zhejiang, China - Focusing on Older Adults’ Needs, Spatial Environment, and Sustainable Design -
중국 저장성 유휴공간의 노인요양시설 전환에 관한 연구 - 노인의 요구, 공간 환경 및 지속가능성을 중심으로 -
-
Fei Hao, Miryum Chung
하오페이, 정미렴
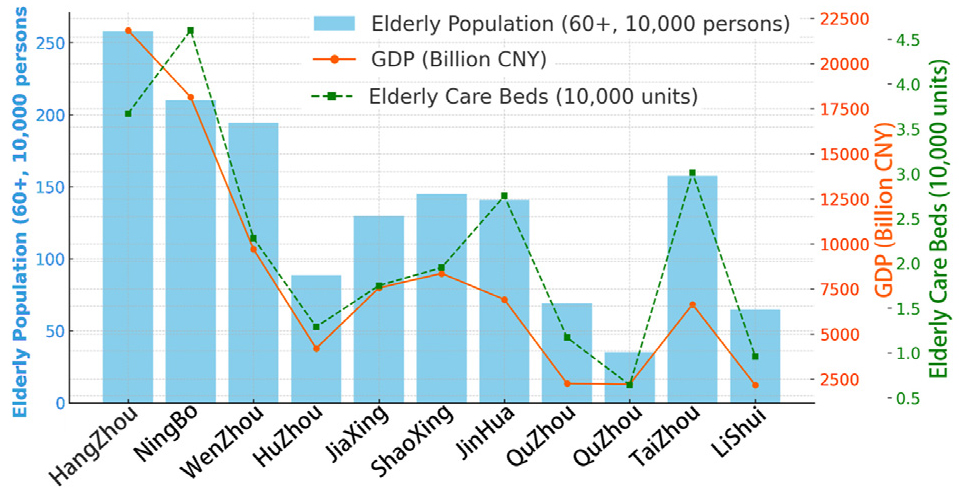
- To address a super-aged society, this study constructs an evaluation framework-derived from prior research-along two core dimensions: older adults’ physiological, social, and …
- To address a super-aged society, this study constructs an evaluation framework-derived from prior research-along two core dimensions: older adults’ physiological, social, and psychological needs, and spatial environment and sustainability design. It then conducts qualitative analyses of three Zhejiang cases of idle spaces (a vacant primary school, a community center, and a department store) undergoing elderly care facility conversion, and obtains five experts’ Likert five-point ratings on the same framework as an expert evaluation. Cross-validating case and expert results reveals marked type differences in spatial adaptability and subjective experience; common problems include insufficient dispersion of living units, limited spatial flexibility and integration of natural resources, and weakened cultural memory and sense of belonging. The social dimension performs relatively well, whereas sustainability and resilience lag. Implementation-oriented strategies are proposed: refine living units and wayfinding/color zoning; introduce biophilic measures and accessible outdoor areas; embed local culture and mnemonic cues; and use movable partitions/modular furniture with zoned intelligent energy management. - COLLAPSE
-
A Study on Converting Underutilized Spaces into Elderly Care Facilities in Zhejiang, China - Focusing on Older Adults’ Needs, Spatial Environment, and Sustainable Design -
-
Research Article

-
Demand for Housing Support according to the Housing Relocation Plan of Young Single-Family Households in Seoul by Age Group
서울시 청년 1인가구의 연령대별 주거 이동 계획에 따른 주거지원 수요 탐색
-
Sung-Chan Hong, Tae-Seok Sim, Woo-Min Jung, Yoonseo Lee
홍성찬, 심태석, 정우민, 이윤서
- This study examines differences in housing satisfaction, neighborhood satisfaction, and awareness of housing support programs among young single-person households in Seoul, categorized …
- This study examines differences in housing satisfaction, neighborhood satisfaction, and awareness of housing support programs among young single-person households in Seoul, categorized by age and by whether they plan to relocate. The findings show that residential relocation plan is strongly associated with economic capacity: individuals with higher income and education levels were more likely to plan a move and were concentrated in officetels and multifamily units, while non-movers were more often in detached multi-household dwellings. Dissatisfaction factors varied by age. Those aged 19-24 expressed concerns about basic housing conditions, while the 25-29 group emphasized noise, safety, and sanitation issues. For the 30-34 group, overall housing and neighborhood satisfaction were most closely linked to moving intention. Support needs also differed across ages, ranging from rent subsidies for younger respondents to Jeonse and home-purchase assistance for older youth. However, awareness of housing support programs remained low in all groups. These results highlight the need for differentiated, age-specific housing policies that address diverse living conditions and support demands among young single-person households. - COLLAPSE
-
Demand for Housing Support according to the Housing Relocation Plan of Young Single-Family Households in Seoul by Age Group
-
Research Article
-
Spatial Planning Characteristics of Intergenerational Housing Complexes in Japan - An Exploratory Multiple-Case Study by Interaction Type -
일본 세대교류형 주거단지의 공간 계획 특성에 관한 연구 - 교류유형별 탐색적 다중사례연구 -
-
Ha-Yeon Lee, Jeong-Min Moon
이하연, 문정민
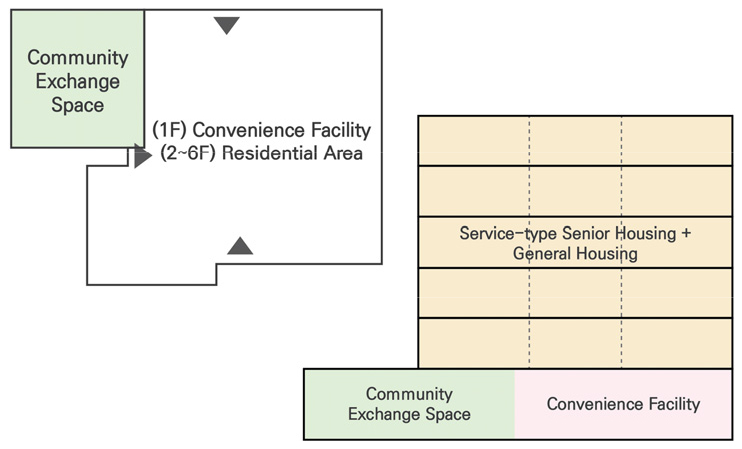
- This study examines intergenerational housing as a model to address the growing demand for social care and the issues of isolation associated …
- This study examines intergenerational housing as a model to address the growing demand for social care and the issues of isolation associated with aging and the rise of single-person households. Three Japanese housing complexes, selected for their demographic and policy similarities to Korea, were analyzed through floor plan analysis, field observation, and interviews with facility managers to identify spatial characteristics by types of intergenerational interaction. The findings show that planned interaction depends on programs and linkages with local facilities; incidental interaction is shaped by the density of entrances, contact spaces, and amenity layouts; active interaction is enhanced through flexible layouts, movable partitions, and multifunctional furniture; and indirect interaction is supported by visual and auditory openness through architectural elements such as courtyards and glass façades. These complexes also combine rental and ownership units to support life-cycle residential circulation and promote Aging in Community (AIC). The study highlights the spatial characteristics of intergenerational housing and calls for further empirical research for its application in the Korean context. - COLLAPSE
-
Spatial Planning Characteristics of Intergenerational Housing Complexes in Japan - An Exploratory Multiple-Case Study by Interaction Type -
-
Research Article

-
A Study on Residential Environment Factors Influencing Residential Satisfaction - Focusing on a Comparative Analysis of the M and Z Generations -
주거환경 만족도에 영향을 미치는 주거환경요인에 관한 연구 - M세대와 Z세대의 비교분석을 중심으로 -
-
Keun-Oh Park
박근오
- The MZ generation exhibits distinct characteristics compared to the older generations and is rapidly emerging as a key demand group in the …
- The MZ generation exhibits distinct characteristics compared to the older generations and is rapidly emerging as a key demand group in the future housing market. This study aims to comparatively analyze the key factors influencing residential environment satisfaction among the Millennial and Gen Z generations. Through this, we seek to propose customized residential environment improvement plans that reflect the unique characteristics and housing values of each generation. For the analysis, Partial Least Squares (PLS) regression was used to conduct a comparative analysis of the Millennial and Gen Z generations. The results and policy implications are as follows. First, due to significant differences in demographics, economic status, and living environments, a differentiated strategy is needed for each generation. Second, both Millennials and Gen Z consider the accessibility of housing and commercial facilities to be important. Third, apart from common factors, education emerged as a key concern for Millennials, while Gen Z placed a high value on the accessibility of medical facilities. Fourth, differences were found between the two generations in terms of community composition. This study is significant for its analysis of the factors influencing residential satisfaction, differentiating between the Millennial and Gen Z generations to propose targeted improvement strategies. Therefore, its findings can serve as foundational data for future policy-making aimed at improving generational housing environments. - COLLAPSE
-
A Study on Residential Environment Factors Influencing Residential Satisfaction - Focusing on a Comparative Analysis of the M and Z Generations -
-
Research Article
-
A Comparative Study of Global Policies to Develop Models of Aging in Community - Focus on UK, Denmark and Japan -
Aging in Community 구축을 위한 해외 정책 비교 분석 - 영국, 덴마크, 일본을 중심으로 -
-
Seong Wook Lee, Seo Ryeung Ju, Yi-Kyung Hong
이성욱, 주서령, 홍이경
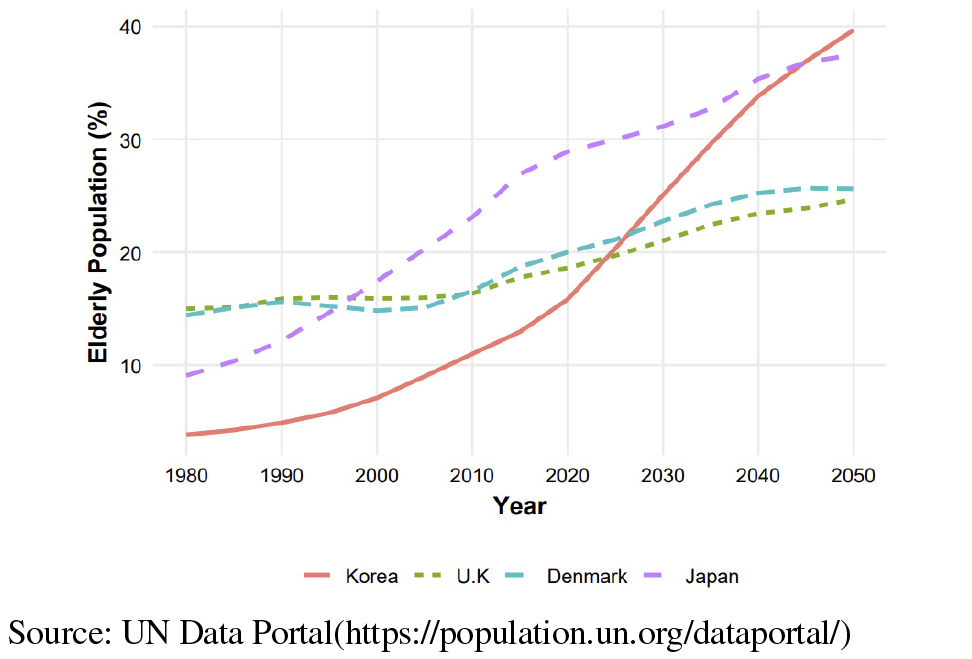
- This study aims to draw key policy implications for designing a successful Aging in Community (AIC) model for South Korea. To achieve …
- This study aims to draw key policy implications for designing a successful Aging in Community (AIC) model for South Korea. To achieve this, it conducts a comparative analysis of the AIC policies in the United Kingdom, Denmark, and Japan—countries with earlier experiences in managing aged populations. For its research method, policy documents from the three nations were compared using a six-factor analytical framework: (1) Legal basis & Policy, (2) Financing & Cost burden, (3) Living area scope & Physical Environment, (4) Community social services, (5) Housing supply & Maintenance, and (6) Workforce development & Composition.The findings reveal that while each country’s approach is deeply rooted in its distinct welfare philosophy—the UK’s means-tested selective model, Denmark’s tax-based universalism, and Japan’s social insurance-based hybrid system—they converge on several key principles. All three nations have established integrated governance to overcome service fragmentation, legally defined care as a right, and adopted prevention and rehabilitation as a core strategy to enhance seniors’ independence and ensure long-term fiscal sustainability.This study concludes by proposing a strategic direction for a Korean AIC model, emphasizing the need for rights-based integrated governance and a sustainable financing model. Furthermore, it highlights the importance of a service paradigm centered on prevention—supported by diverse housing models, regionally-tailored spatial strategies, and a professionalized workforce. - COLLAPSE
-
A Comparative Study of Global Policies to Develop Models of Aging in Community - Focus on UK, Denmark and Japan -
-
Research Article
-
A Study on the Introduction of the University-Based Retirement Community (UBRC) Model - Trend Analysis of Housing Intentions and Service Needs of Middle-Aged and Older Adults -
대학연계형 고령친화 주거단지(UBRC) 모델 도입 연구 - 중・고령자의 거주의향 및 서비스 요구의 경향 분석 -
-
Youngho Ko
고영호
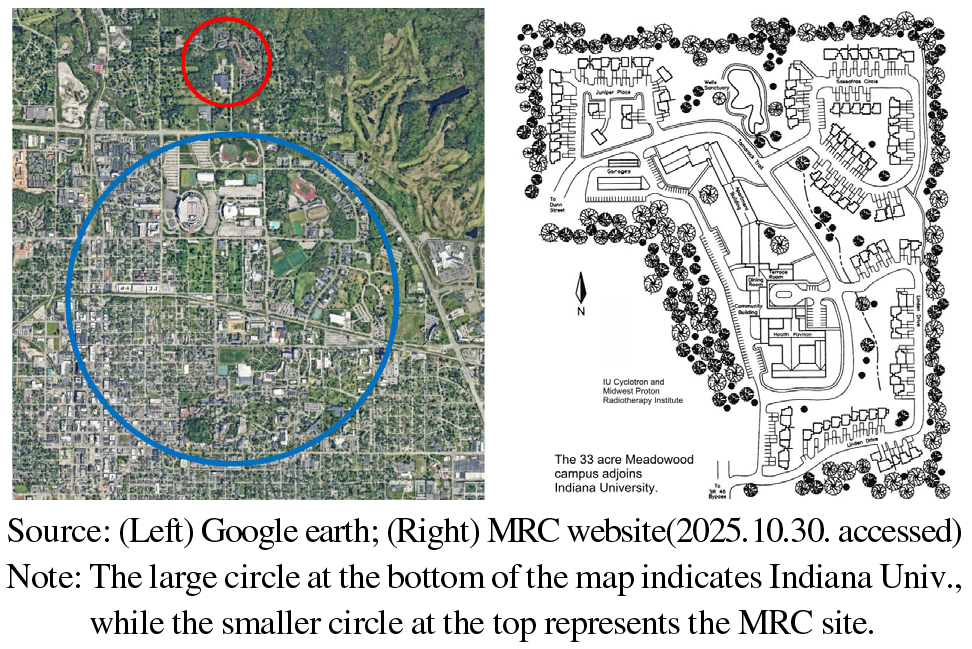
- This study examines the potential introduction of the University-Based Retirement Community (UBRC) model in Korea and analyzes the overall trends in housing …
- This study examines the potential introduction of the University-Based Retirement Community (UBRC) model in Korea and analyzes the overall trends in housing intentions and service needs among middle-aged and older adults. After reviewing the concept and development of UBRCs—integrated housing models that link university facilities with health, daily living, and educational resources—this study conducted an online survey of 500 adults aged 50–69. The results indicate a generally high level of interest in UBRC residency, particularly for communities located on or near university campuses. Respondents expressed strong expectations for convenient daily living, essential health and emergency services, and practical support services such as cleaning and laundry. Interest in educational programs and opportunities for social participation with universities was also substantial. These findings suggest that UBRCs may serve as an age-friendly housing model that supports both residential stability and active engagement in later life. For initial implementation, pilot projects could prioritize demographic groups demonstrating relatively higher interest, while long-term strategies may expand inclusively to diverse older populations. Overall, this study provides foundational evidence for UBRC planning in the context of Korea’s rapidly aging society. - COLLAPSE
-
A Study on the Introduction of the University-Based Retirement Community (UBRC) Model - Trend Analysis of Housing Intentions and Service Needs of Middle-Aged and Older Adults -
-
Research Article

-
Determinants of Housing Size Across the Life Cycle - Evidence from the 2010 Recession and the 2020 Boom -
생애주기별 주택규모 결정요인 분석 - 2010년 쇠퇴기와 2020년 호황기 비교를 중심으로 -
-
Esther Jun, Hwan-yong Kim
전에스더, 김환용
- This study examines determinants and temporal changes in housing size by life cycle stage using 2010 and 2020 Korea Housing Survey data. …
- This study examines determinants and temporal changes in housing size by life cycle stage using 2010 and 2020 Korea Housing Survey data. The two periods represent contrasting market conditions: the post-global financial crisis downturn and the asset market boom following COVID-19. Household economic capacity (permanent income, net assets, real estate asset ratio), housing costs, tenure type, housing type, and residential location (Seoul Metropolitan Area vs. non-metropolitan areas) were analyzed for their effects on housing size. Net assets and housing type consistently emerged as key determinants, with asset-based influence strengthening in 2020. Housing costs and income effects declined, while residence in the Seoul Metropolitan Area consistently reduced housing size. Life cycle transition analysis showed that moving to a higher stage over ten years increased the influence of net assets and housing type, with stronger constraints from metropolitan residence. These findings highlight that market cycles and life cycle transitions jointly reshape housing size determination, calling for tailored housing supply and financial support policies, alongside measures to improve residential conditions across regions. - COLLAPSE
-
Determinants of Housing Size Across the Life Cycle - Evidence from the 2010 Recession and the 2020 Boom -
-
Research Article
-
A Case Study on the Development of Community Care Village Maps
커뮤니티 케어 마을지도 개발에 관한 사례 연구
-
Ok Hee An, Hyun-ju Lee
안옥희, 이현주
- Recently, the number of ways in which residents directly discover and collect information on various regional issues such as welfare, education, and …
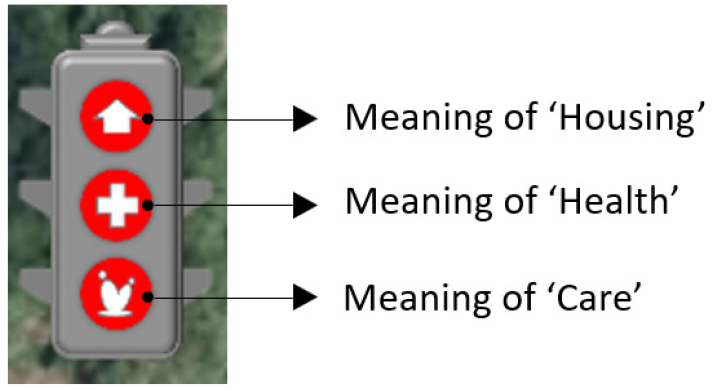
- Recently, the number of ways in which residents directly discover and collect information on various regional issues such as welfare, education, and culture to solve problems is increasing, and online activities to share this process with many people online are actively taking place. In this way, we tried to find a way to increase efficiency by applying the region-led problem-solving method to the community care policy of an ultra-aged society. In this study, housing, health, and care areas were investigated through interviews with local residents and local leaders of basic organizations in Gyeongsan-si, Goryeong-gun and Yeongcheon-si. And by visualizing the traffic light model, a community care village map was developed so that the necessary areas of service can be easily identified at a glance. The three colors of traffic lights were classified into housing, health, and care, and red (high risk), yellow (normal risk), and green (low risk) were defined according to the risk level for each area. It is expected to be used as basic data for providing regional-specific services through continuous understanding of the current status through follow-up surveys, online use, and establishment of a connection system with related organizations. - COLLAPSE
-
A Case Study on the Development of Community Care Village Maps
-
Research Article
-
Price Estimation by Type of AI Smart Housing Service Using PSM
PSM을 활용한 AI 스마트 주거서비스 유형별 가격추정
-
Yongkyung Cho
조용경
- Due to demographic shifts and increasing GDP per capita, housing demands have become more diverse and complex. As people seek higher quality …
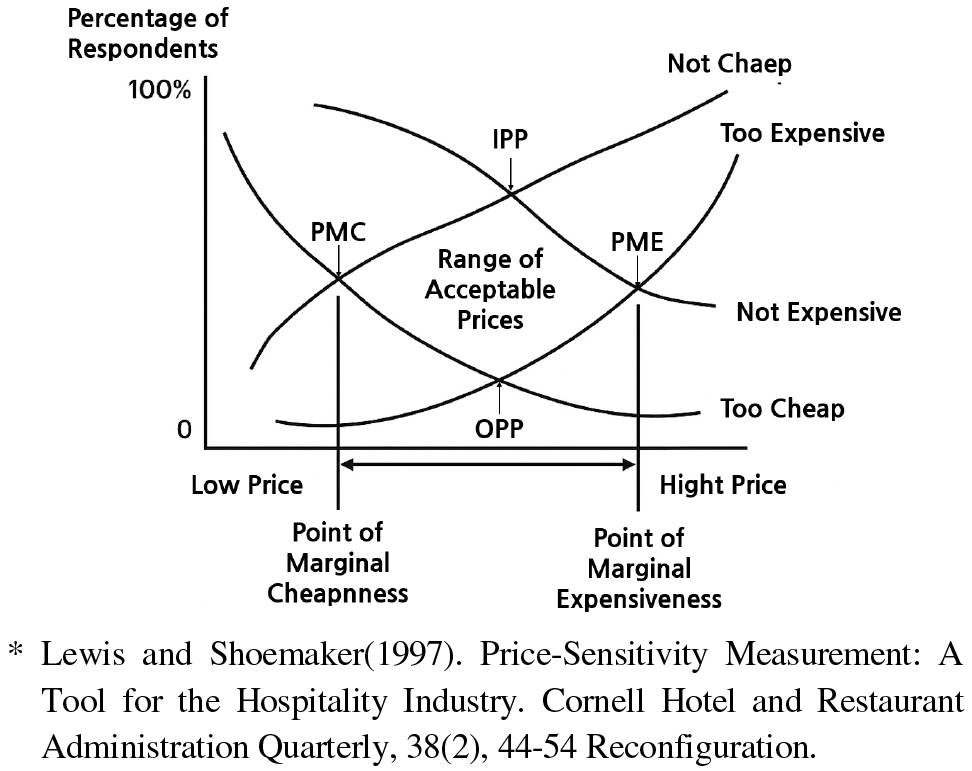
- Due to demographic shifts and increasing GDP per capita, housing demands have become more diverse and complex. As people seek higher quality of life, the need for innovative housing services has grown. Advances in smart technologies now enable cost-effective and varied housing services that were previously difficult or expensive to provide. However, market remains underdeveloped, mainly due to mismatches between consumer demand and supplier offerings—including acceptable payment levels. This study aims to estimate appropriate prices for AI Smart Housing services using the Price Sensitivity Measurement (PSM) method. Results show that the ‘Living Support Service’ had the highest acceptable price range (12,000-19,500 KRW/Month) with an Ideal Price Point (IPP) of 14,700 KRW/Month, followed by ‘Security and Safety Services’ (11,200-14,200 KRW/Month, IPP 11,200 KRW/Month), ‘Healthcare Services’ (9,300-14,000 KRW, IPP 9,500 KRW), ‘Emotional and Community Services’ (9,300-11,000 KRW/Month, IPP 9,300 KRW/Month), and ‘Energy-Saving Services’ (5,400-9,700 KRW/Month, IPP 7,200 KRW/Month). Among all types, energy-saving services showed the lowest price sensitivity, followed by emotional and community, security and safety, healthcare, and living support services. These findings provide a pricing guideline for developing market-acceptable AI Smart Housing services and can be used as a reference for commercialization strategies or public housing policy planning. - COLLAPSE
-
Price Estimation by Type of AI Smart Housing Service Using PSM
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of the Korean Housing Association
Journal of the Korean Housing Association
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of the Korean Housing Association
Journal of the Korean Housing Association









